The imminent phase-out of third-party cookies by Google Chrome marks a significant turning point for digital marketing as we know it today. This shift might seem daunting, but it’s not cause for alarm. Instead, it presents an opportunity for innovation and adaptation. In this article, we’ll dive into the ramifications of this change, armed with comprehensive insights gathered through discussions with our digital marketing platform representatives.
💡 Tip: Watch our on-demand webinar: Preparing Digital Marketing Strategies for a Cookieless Future!
Table of Contents:
Video: What Digital Marketers Need to Know About Google Third-Party Cookie Deprecation
What is Google Chrome's Third-Party Cookie Deprecation
The Distinction Between Cookie Types
The Rising Importance of First-Party Data
When is Google Deprecating Third-Party Cookies
How Does This Change Impact Digital Marketing Channels?
Google Ads
Microsoft Ads
Meta Ads
LinkedIn Ads
Programmatic - StackAdapt
CallRail Call Tracking
Conclusion
Video: What Digital Marketers Need to Know About Google Third-Party Cookie Deprecation
What is Google Chrome’s Third-Party Cookie Deprecation?
You might already be familiar with the buzz around Google Chrome’s decision to phase out third-party cookies. Google is eliminating the use of third-party cookies in its Chrome browser, a move that aligns with the industry's growing emphasis on enhancing user privacy and online data protection. This decision by Chrome, following in the footsteps of Safari and Firefox, will change how marketers approach digital advertising.
The Distinction Between Cookie Types
A “cookie” is a small file of information stored in the browser when a user visits a website. The cookie deprecation targets third-party cookies, which are stored by a service that operates across multiple sites. For example, an ad platform might store a cookie when you visit a news site. These cookies are commonly used for tracking users across the web, facilitating cross-site advertising and analytics.
Conversely, first-party cookies, which are stored by the site you are directly engaging with, will not be affected by this phase-out. These cookies are fundamental to creating a seamless user experience, supporting functions like user login authentication, preference settings, and managing shopping cart contents.
The Rising Importance of First-Party Data
The role of first-party cookies and the data they collect is expected to become increasingly important. This shift to relying more on first-party data — information that is gathered directly from your audience with their explicit consent — is indicative of a larger trend toward fostering privacy-centric, consent-based interactions between websites and their users. For marketers and website owners, this means adapting strategies to better utilize first-party cookies and data.
When is Google Deprecating Third-Party Cookies?
Starting in Q1 2024, Google disabled third-party cookies for 1% of Chrome Stable users. The full deprecation is set to be completed by 2025 (delayed from the previously announced date of 2024).
How Does This Change Impact Digital Marketing Channels?
In response to the upcoming deprecation of third-party cookies on Google Chrome, our team set out to determine the anticipated impact across each of our digital marketing channels. We sought insights directly from channel representatives from Meta, Google, LinkedIn, StackAdapt, Microsoft, and CallRail.
We’ll first start by diving into Google Ads:
- Google Ads Tags - No Impact
The Google Ads tag operates as a first-party cookie, ensuring it remains unaffected by third-party cookie deprecation. This means tracking and ad delivery through Google Ads tags will continue as usual.
- Google Ads Reporting (Tag-Based Conversion Measurement) - Low Impact
While the core functionality of measuring conversions will remain intact due to the first-party nature of the cookie, nuances in attribution and multi-touch data may experience some disruptions. This could slightly affect the precision of tracking users' paths through the conversion funnel. However, Enhanced Conversions could help minimize the amount of data lost when third-party cookies are entirely deprecated.
- Audiences - Low-Medium Impact
- Detailed Demographics, In-Market, Affinity, and Custom/Combined - Low to Medium Impact
While we expect these audiences to still exist, it’s unclear to what extent their effectiveness and reach may be impacted. Privacy Sandbox solutions such as the Topics API will likely continue to empower these audiences.
- Detailed Demographics, In-Market, Affinity, and Custom/Combined - Low to Medium Impact
- First-Party Data from CRMs - No Impact
Leveraging first-party data sourced from Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems remains a strong and unaffected strategy. This data type is crucial for tailoring and personalizing your digital marketing efforts moving forward.
- Remarketing Audiences - Low Impact
Remarketing strategies that utilize tag-based audiences to target users based on their interactions with your website will continue to function. However, the scope for serving ads to these users on the Google Display Network (GDN) might see some constraints, potentially limiting reach and frequency.

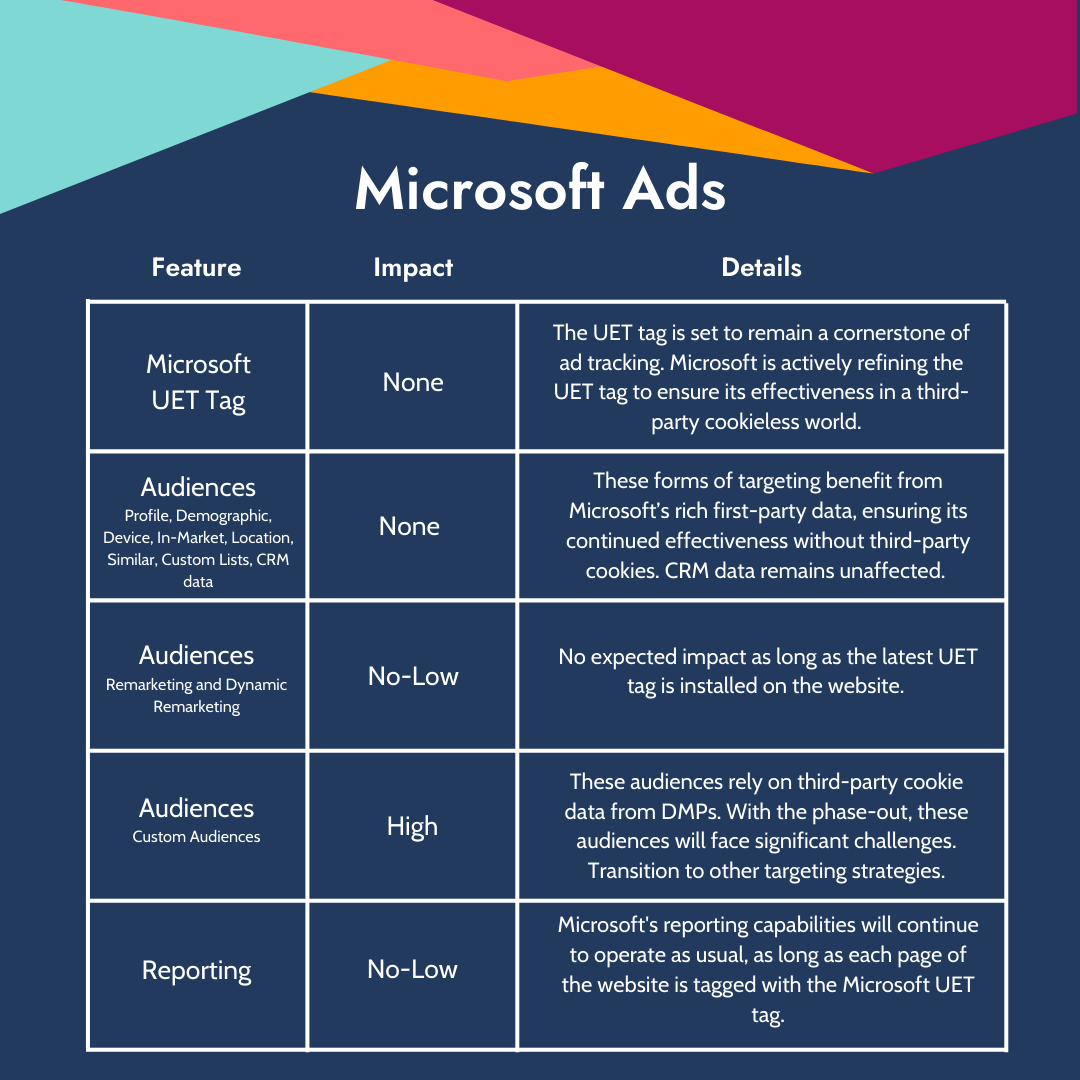
Microsoft Ads:
- Microsoft UET Tag - No Impact
The Universal Event Tracking (UET) tag is set to remain a cornerstone of Microsoft Ads tracking. Microsoft is actively refining the UET tag to ensure its effectiveness in a third-party cookieless world.
- Audiences:
- LinkedIn Profile Targeting - No Impact
This form of targeting benefits from Microsoft's rich first-party data, ensuring its continued effectiveness without third-party cookies.
- Demographic, Device, Location, Language Targeting - No Impact
These targeting options also leverage Microsoft's first-party data, guaranteeing their ongoing viability.
- In-Market Audiences - No Impact
Again, Microsoft's first-party data underpins these audiences, ensuring their stability in a cookieless environment.
- Similar Audiences - No Impact
Provided that sites are properly tagged with the latest UET JavaScript Tag, similar audiences will continue to be effectively targeted.
- Custom Combination Audience Lists - No Impact
As with the other audience types, these lists remain unaffected, thanks to the reliance on Microsoft's first-party data.
- Remarketing and Dynamic Remarketing Audiences - No-Low Impact
No expected impact as long as the latest UET tag is in use.
- Custom Audiences - High Impact
The exception comes with Custom Audiences, which rely on third-party cookie data from data management platforms. With the phase-out of third-party cookies, these will face significant challenges. Transitioning to Customer Match targeting is recommended as an alternative strategy.
- First-Party Data from CRMs - No Impact
First-party data integration from CRM systems remains unaffected, highlighting the importance of leveraging direct customer relationships.
- LinkedIn Profile Targeting - No Impact
- Microsoft Reporting - No -Low Impact
Microsoft's reporting capabilities will continue to operate as usual, as long as each page of the website is tagged with the Microsoft UET tag.
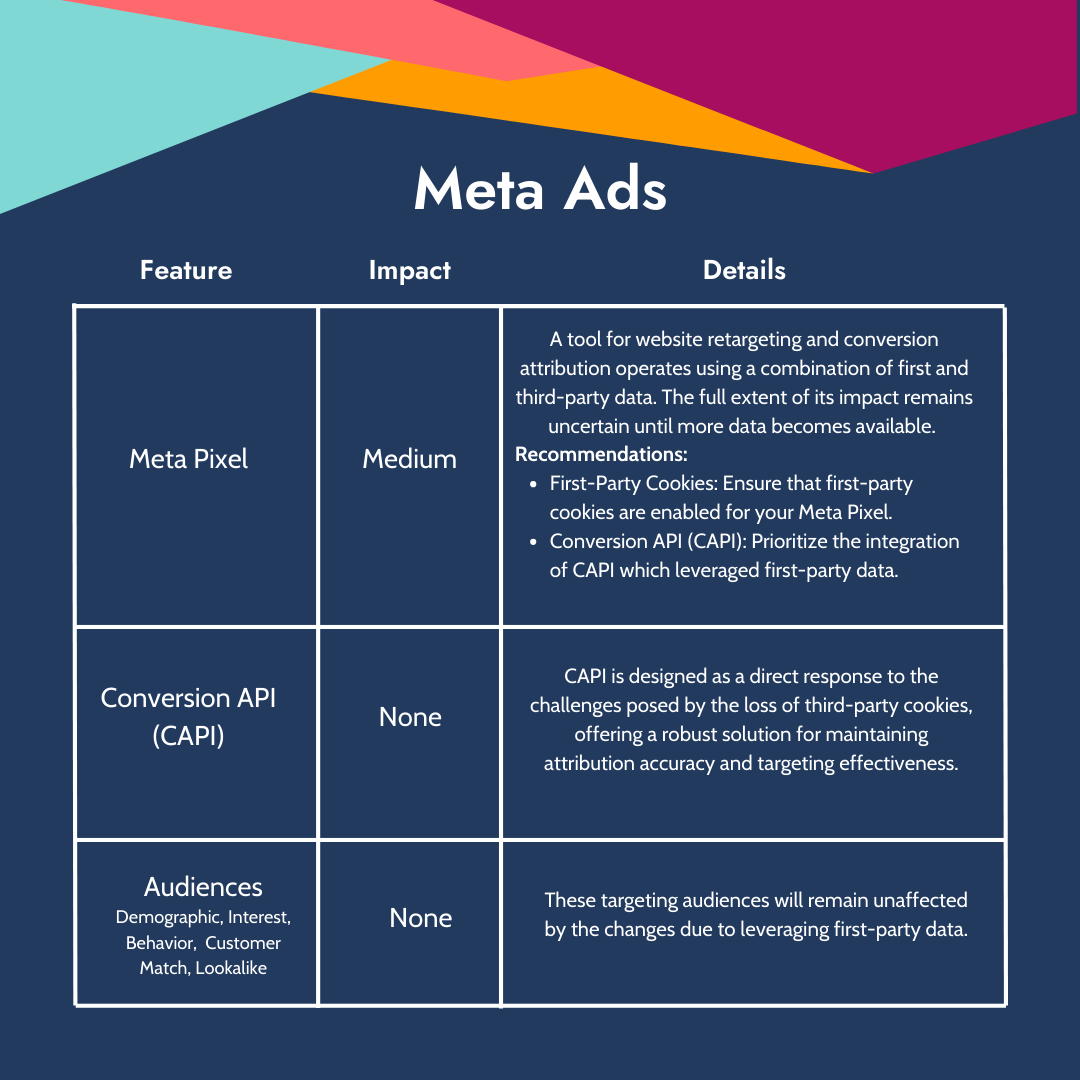
Meta Ads:
- Meta Pixel (retargeting and conversion attribution) - Medium Impact
The Meta Pixel, a tool for website retargeting and conversion attribution, operates using a combination of first and third-party cookies. The full extent of its impact in a post-third-party cookie world remains uncertain until more data becomes available or until Meta provides further guidance. However, Meta's strong advocacy for the adoption of the Conversion API (CAPI) suggests a potential impact on the Pixel's effectiveness.
- Recommendations:
First-Party Cookies: Ensure that first-party cookies are enabled for your Meta Pixel. This can be done within the Events Manager by navigating to Data Sources > Settings > Cookie Usage.
Conversion API (CAPI): Prioritize the integration of the Conversion API, which facilitates the server-side transmission of first-party data from your website to Meta, aiding in attribution and targeting without relying on third-party cookies.
- Conversion API (or CAPI) - No Impact
The Conversion API is designed as a direct response to the challenges posed by the loss of third-party cookies, offering a robust solution for maintaining attribution accuracy and targeting effectiveness.
- Audiences:
- Demographic, Interest, and Behavior Targeting - No Impact
These targeting options are powered by data users share on Facebook and Instagram, making them unaffected by the shift away from third-party cookies.
- Customer Match Audiences - No Impact
Built on first-party data, Customer Match Audiences will continue to be a valuable targeting tool, unaffected by the changes.
- Lookalike (or similar) Audiences - No Impact
Lookalike audiences leverage the same first-party data that informs demographic, interest, and behavior targeting, ensuring their continued effectiveness.
- Demographic, Interest, and Behavior Targeting - No Impact
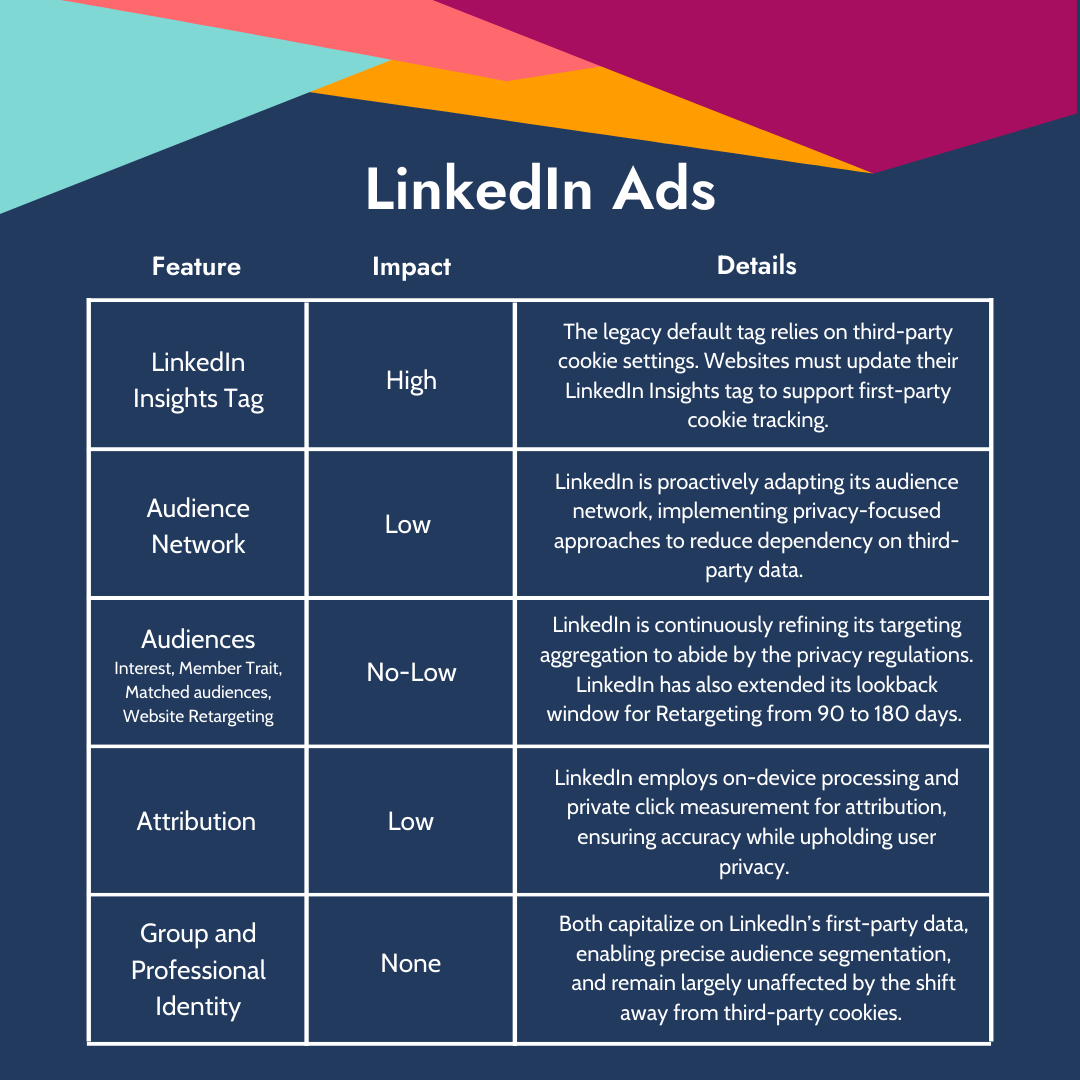
LinkedIn Ads:
- LinkedIn Insights Tag - High Impact
The legacy default for the LinkedIn Insights Tag relies on third-party cookie settings, which are increasingly being blocked by browsers. To maintain effective conversion tracking, websites must update their LinkedIn Insights Tag to support first-party cookie tracking. Additionally, other enhancements to keep in mind are offline conversion tracking, revenue attribution reporting, and CRM sync for company engagement reporting.
- LinkedIn Audience Network - Low Impact
LinkedIn is proactively adapting its Audience Network, implementing privacy-focused approaches to reduce dependency on third-party data. This initiative reflects LinkedIn's commitment to privacy while striving to maintain the effectiveness of its advertising network.
- Interest Targeting & Member Trait Audiences - Low Impact
Recent updates to LinkedIn's interest targeting and member trait audiences have reduced their reliance on app-based activity alone. These changes aim to preserve the precision of audience targeting amidst evolving privacy standards.
- Matched Audiences - Low to No Impact
LinkedIn has introduced additional compliance guardrails around the use of matched audiences. These measures are designed to ensure adherence to privacy regulations without significantly impacting the utility of matched audiences for advertisers.
- Website Retargeting - Low Impact
To compensate for potential limitations in retargeting capabilities, LinkedIn has extended its lookback window for website retargeting from 90 to 180 days. Additionally, new retargeting methods based on platform engagement have been introduced, enhancing the ability to capture broader retargeting pools.
- Group Identity - No Impact
Group Identity capitalizes on LinkedIn's extensive first-party data, grouping members with similar professional attributes for targeted advertising. This approach prioritizes privacy, minimizing the sharing of personal information while facilitating effective ad delivery.
- Attribution - Low Impact
LinkedIn employs on-device processing and private click measurement for attribution, ensuring accuracy while upholding user privacy. These techniques represent LinkedIn's investment in privacy-safe attribution methodologies.
- Professional Identity - No Impact
LinkedIn's strategy for professional identity leverages a multi-faceted data approach, including member profiles, platform engagement, the LinkedIn identity graph, the insight tag with first-party cookies, and CRM data. This rich data ecosystem enables precise audience segmentation based on professional traits and buyer intent, largely unaffected by the shift away from third-party cookies.
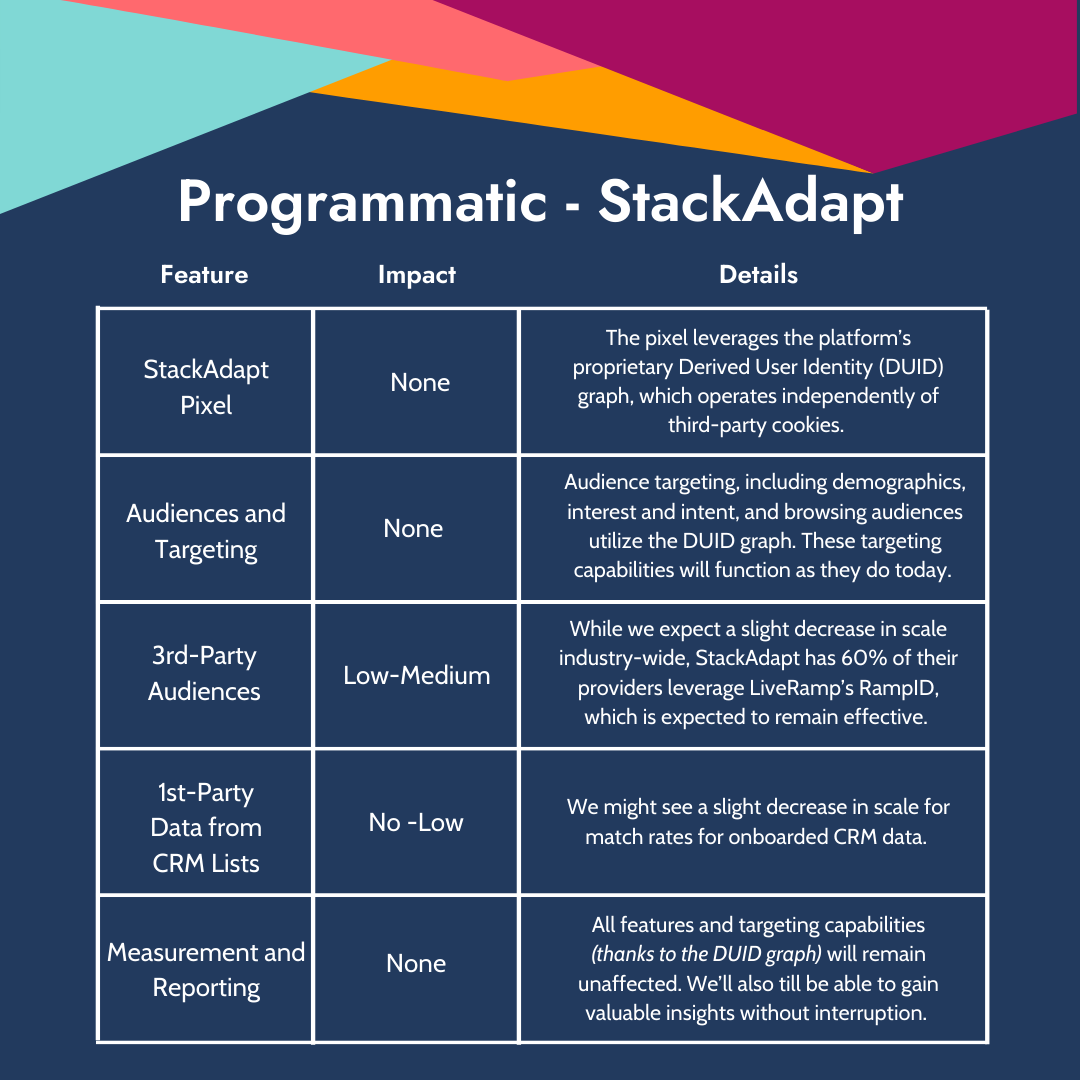
Programmatic - StackAdapt:
- StackAdapt Pixel - No Impact
The StackAdapt Pixel leverages the platform's proprietary Derived User Identity (DUID) Graph, an innovative ID graph that operates independently of third-party cookies. This ensures the continued accuracy and scalability of audience targeting without any anticipated impact.
- StackAdapt Audiences and Targeting (Demographics, HHI, Interest & Intent, Browsing Audiences) - No Impact
Audience targeting within StackAdapt, including demographics, household income (HHI), interest and intent, and browsing audiences, utilizes the DUID. This means these targeting capabilities will remain unaffected, functioning just as effectively as they do today.
- 3rd-party Audiences - Low-Medium Impact
While a slight decrease in scale for third-party data is expected industry-wide—particularly from providers reliant on third-party cookies—StackAdapt's access to over 350 data providers mitigates this concern significantly. Notably, over 60% of these providers use LiveRamp's RampID, a persistent identifier that will continue to be effective post-cookie deprecation. For the remaining providers, StackAdapt is actively working to support alternative, cookie-proof identifiers, ensuring minimal disruption.
- First-party data from CRM Lists - No to Low Impact
We may see a slight decrease in scale for match rates for onboarded customer relationship management (CRM) data. Stack Adapt is working on integrating additional CRM onboarding partners to supplement our in-house solution with the goal of maintaining or improving match rates.
- In-platform measurement and targeting solutions - No Impact
StackAdapt's suite of in-platform solutions, including ABM targeting and measurement, foot traffic attribution, brand lift, and first-party data attribution, are all powered by the DUID. As such, they will continue to operate seamlessly without impact.
- Reporting - No Impact
StackAdapt's reporting features will remain fully functional, providing valuable insights and analytics without interruption.
CallRail Call Tracking:
- Call Tracking - Keyword Pools - No Impact
Despite the industry-wide shift away from third-party cookies, CallRail's keyword pools, which rely on first-party data, will not be impacted and will continue to attribute calls to their original sources as they do now.
Given the deprecation of third-party cookies, integrating call tracking with CallRail (or another service provider of your choice) is more important than ever, offering a vital means to compensate for the loss of third-party cookie data by capturing valuable insights directly from phone interactions.

Conclusion
The deprecation of third-party cookies marks both an end and a beginning in your digital marketing strategies. While traditional methods of tracking and targeting are transforming, this change is a time for innovation and a focus on privacy-focused marketing strategies. The insights from platforms like Google Ads, LinkedIn, Meta, StackAdapt, and CallRail demonstrate proactive adaptation to these changes, ensuring that marketers have the tools and strategies they need to continue engaging their audiences effectively. Embracing first-party data, enhancing direct customer relationships, and leveraging technology like Enhanced Conversions and call tracking is key to growing in this new environment.
The focus on privacy, transparency, and user consent will not only comply with regulatory changes but also build deeper trust with audiences, laying the foundation for a more sustainable and effective digital marketing ecosystem.
If you have any questions related to strategies in a post-cookie world, feel free to contact us today and receive your free, and personalized, consultation.

