Introduction
Since its release in November 2022, OpenAI’s ChatGPT has had an undeniable impact on the search industry, forcing large tech companies like Google and Meta into reactionary mode as digital marketers scramble to learn how to best leverage this new tool in their daily workflows.
While AI itself has been around in one way or another (even if only conceptually) since the 1950s, OpenAI has officially brought it to the mainstream in a new and exciting way. Their free (for now) bot is capable of writing creatively, translating texts into other languages, generating python scripts, and more.
Even well-known companies like Buzzfeed have been taking advantage of ChatGPT to write web content and perform other marketing-related tasks like SEO and audience research.
But has OpenAI’s groundbreaking language learning model simply expanded the realm of possibilities for SEO professionals and content writers, or has it reduced the need for those roles altogether?
We believe AI does have its place in a digital marketing workflow as long as its limitations and impacts are fully understood.
What is ChatGPT and how does it work?
ChatGPT uses natural language processing, machine learning, and deep learning to auto-generate humanlike text in response to user dialogue. In layman’s terms, users can simply input a prompt, and ChatGPT will generate a response based on its massive array of training data.
Because of its rapid responses and sometimes surprisingly creative tone, ChatGPT has been used to write everything from blog posts and technical guides to emails and social media posts.
The bot isn’t without its flaws though, and we caution users to approach ChatGPT and its AI competitors as personal assistants rather than stand-ins for human writers.
Unpacking Google's stance on AI-generated content
Before this year, Google had long considered content written by AI as being in violation of their spam policy. More recently, however, they updated their developer resources to include search guidance on AI-generated content. In short, Google is no longer explicitly against AI-generated content but remains steadfast in their aim to reward high-quality, human-first content, “however it is produced.”
That being said, chatbots in their current state don’t always get the “human-first” part right, and some of the ethical concerns popping up around how they get and distribute their data may violate Google’s policy on copyright infringement or miss the mark on trustworthiness.
ChatGPT limitations (according to OpenAI)
OpenAI’s model may be the most humanlike chatbot we’ve seen to date, but its creators openly admit to some of the project’s shortcomings. Most notable limitations according to their website:
Lack of fact-checking abilities: ChatGPT can potentially generate plausible-sounding but factually incorrect answers because the bot’s intelligence is limited to the data it receives from its human trainers.
No knowledge of current events: ChatGPT’s training data cuts off in 2021, meaning it is incapable of producing accurate responses to any question that requires an understanding of current events or industry developments from 2022 on, but that won’t stop it from trying.
Inability to ask followup questions to clarify user intent: In its current state, ChatGPT provides responses based on assumed intent, which means queries with multiple meanings or complexities may not receive an ideal output.
AI-generated content: Ethical concerns
Journalists and academics have been quick to point out some of the ethical concerns around artificially intelligent computer models with a capacity for public deception. These concerns also have SEO significance as they relate to Google’s search guidelines and spam policies. Some ethical issues and their SEO implications include:
Plagiarism from other writers
In November 2022, a lawsuit was filed against OpenAI and Microsoft-owned GitHub for scraping copyrighted source code to train AI systems. A group of visual artists filed a similar lawsuit against Stability AI, whose text-to-image generative art model Stable Diffusion scraped billions of images from the web without consent from the original artists.
According to Matthew Butterick, the lawyer assigned to the OpenAI/GitHub case, he has since "heard from people all over the world — especially writers, artists, programmers, and other creators — who are concerned about AI systems being trained on vast amounts of copyrighted work with no consent, no credit, and no compensation."
Potential SEO implications: Google may have evolved their stance on AI-generated content, but they still consider “sites that copy content from other sites, modify it only slightly (for example, by substituting synonyms or using automated techniques), and republish it” to be in violation of their spam policy as it relates to copyright infringement. While the future remains uncertain, the outcomes of these lawsuits might influence Google to take additional measures to identify and penalize AI plagiarism.
Built-in biases and diversity of knowledge
ChatGPT can be a valuable tool for light keyword research thanks to its large dataset, but “large” doesn’t necessarily mean “comprehensive.” In a research paper written by ChatGPT’s creators themselves, they admit that “internet-scale models have internet-scale biases,” such as associating European American names with positive sentiment compared to African American names, and perpetuating negative stereotypes about black women.
These biases exist because well, people are biased. As language learning models function based on probability algorithms, certain voices might be overruled.
Potential SEO implications: An article’s success depends on its ability to reach its target audience. If your target demographic falls outside of ChatGPT’s predominantly white, male, American sample dataset, the output you receive may not speak to your ideal user’s unique pain points. On the flipside, Martech’s list of tools for catching bias in writing can be a great resource for copywriters who already know their target audience but want to make sure their language is objective.
Harmful spread of misinformation
The limitations and ethical concerns outlined above have experts worried about AI further accelerating the proliferation of misinformation on the Internet. In a January 2023 NewsGuard study, analysts prompted ChatGPT to respond to queries related to 100 false news narratives from events occurring before 2021. The bot responded with factually incorrect yet feasible-sounding content – “including detailed news articles, essays, and TV scripts” – for 80 out of 100 false narratives.
For people researching a topic they are unfamiliar with, this false information can easily mislead them into making decisions based on inaccurate perceptions of reality.
Potential SEO implications: Google’s E-E-A-T guidelines consider experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness as primary factors for determining page quality. Sites with false information miss the mark for trustworthiness, a violation holding more weight in some industries than others. In Google’s own words: “On topics where information quality is critically important—like health, civic, or financial information—our systems place an even greater emphasis on signals of reliability.”
Best uses for AI in your content marketing workflow
If used properly and responsibly, AI models make great personal assistants. While its well-documented limitations mean ChatGPT probably can’t out-write your copywriter (yet), the bot can inspire your team to be more creative while making parts of your daily workflow more efficient. Some suggested use cases:
Brainstorming and topic ideation
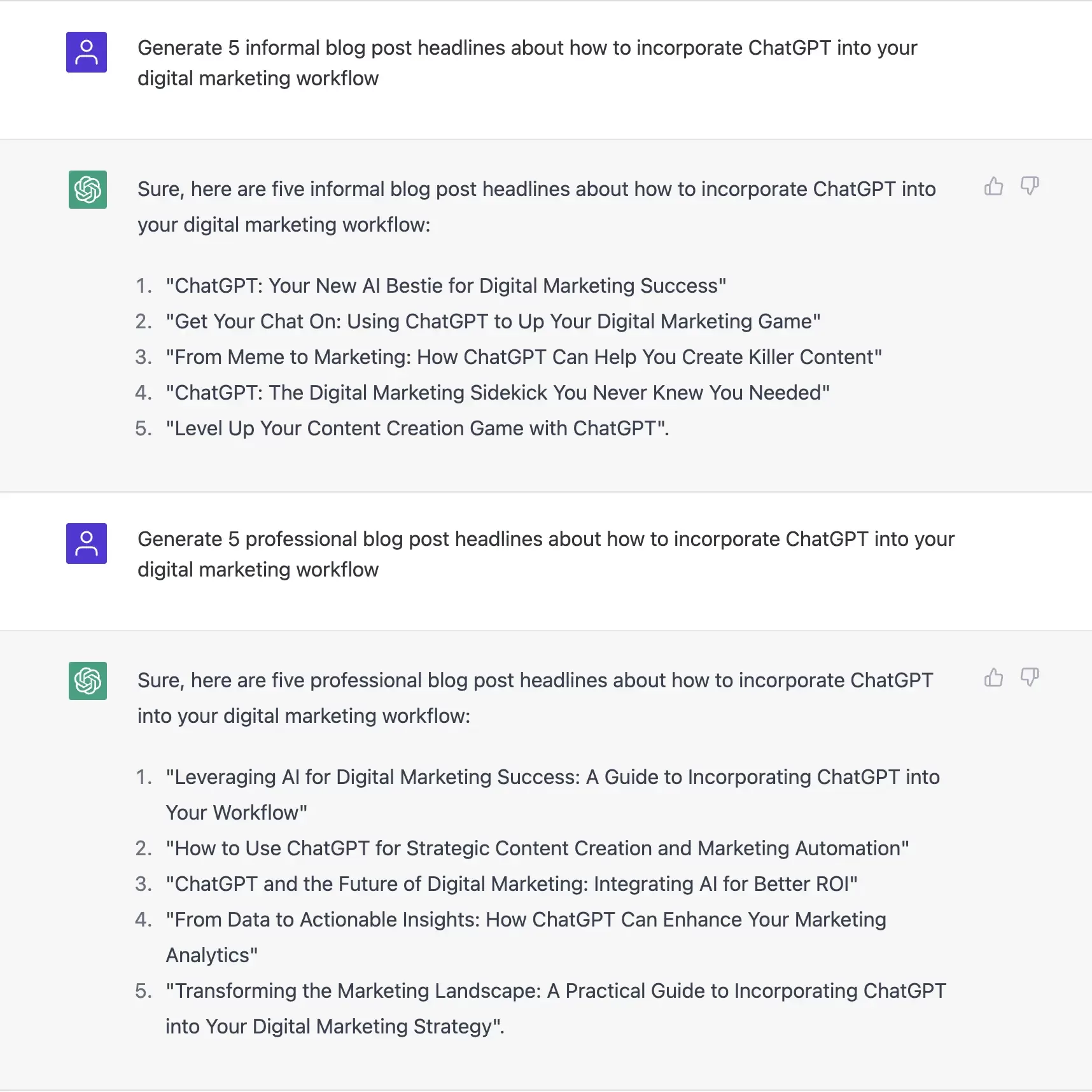
If you have a general topic in mind but need to hone in on something more specific, AI models are great at spitting out potential article titles or blog post outlines. For best results, include an adjective describing the intended tone or voice. As you can see below, adding the word “informal” or “professional” before a blog post headline request makes a huge difference in the results.
Proofreading
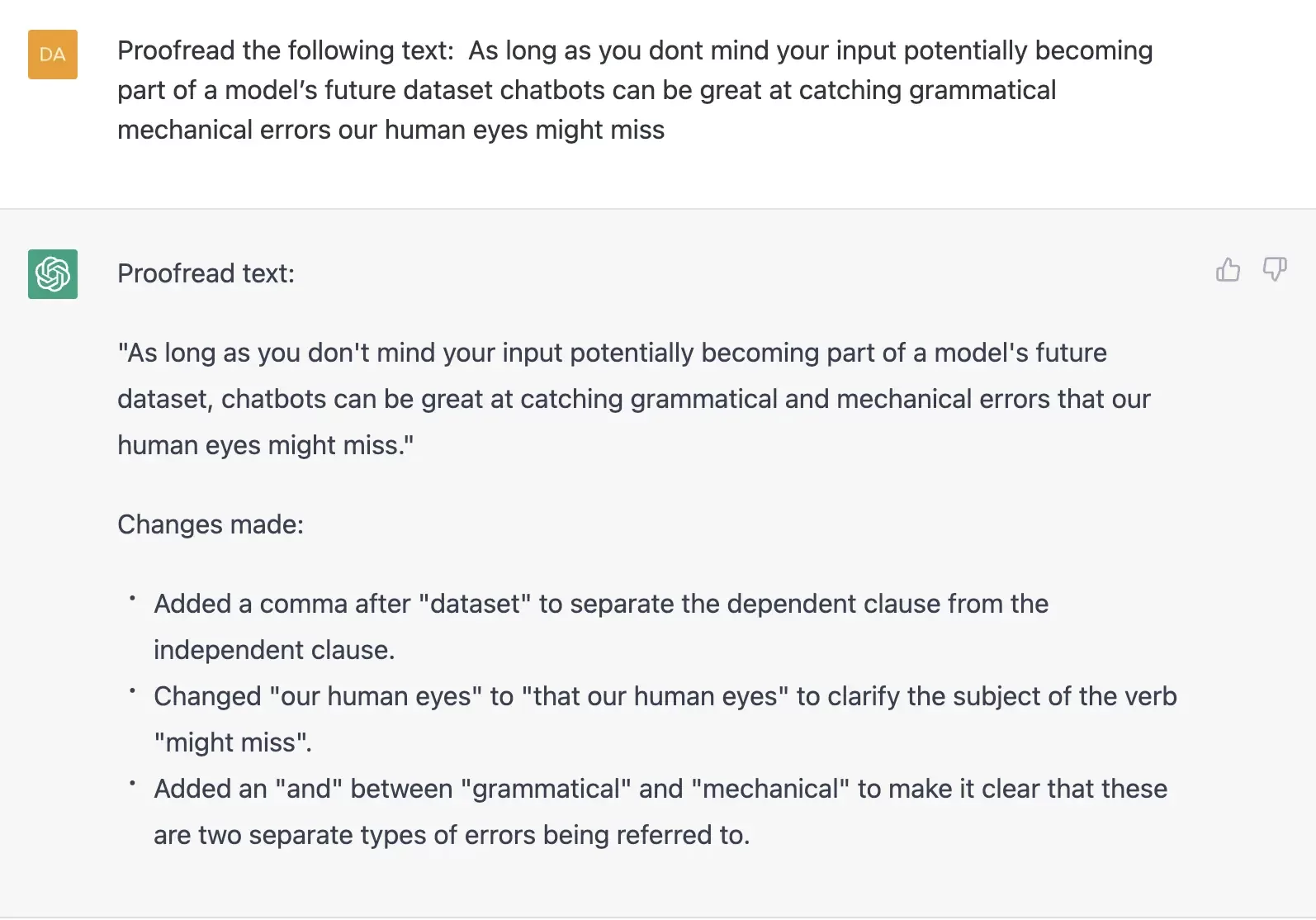
As long as you don’t mind your input potentially becoming part of a model’s future dataset, chatbots can be great at catching the grammatical or mechanical errors our human eyes might miss. Still, we recommend giving your text a final once-over even after your AI proofreader does its job as bots aren’t infallible proofreaders either.
Summarizing
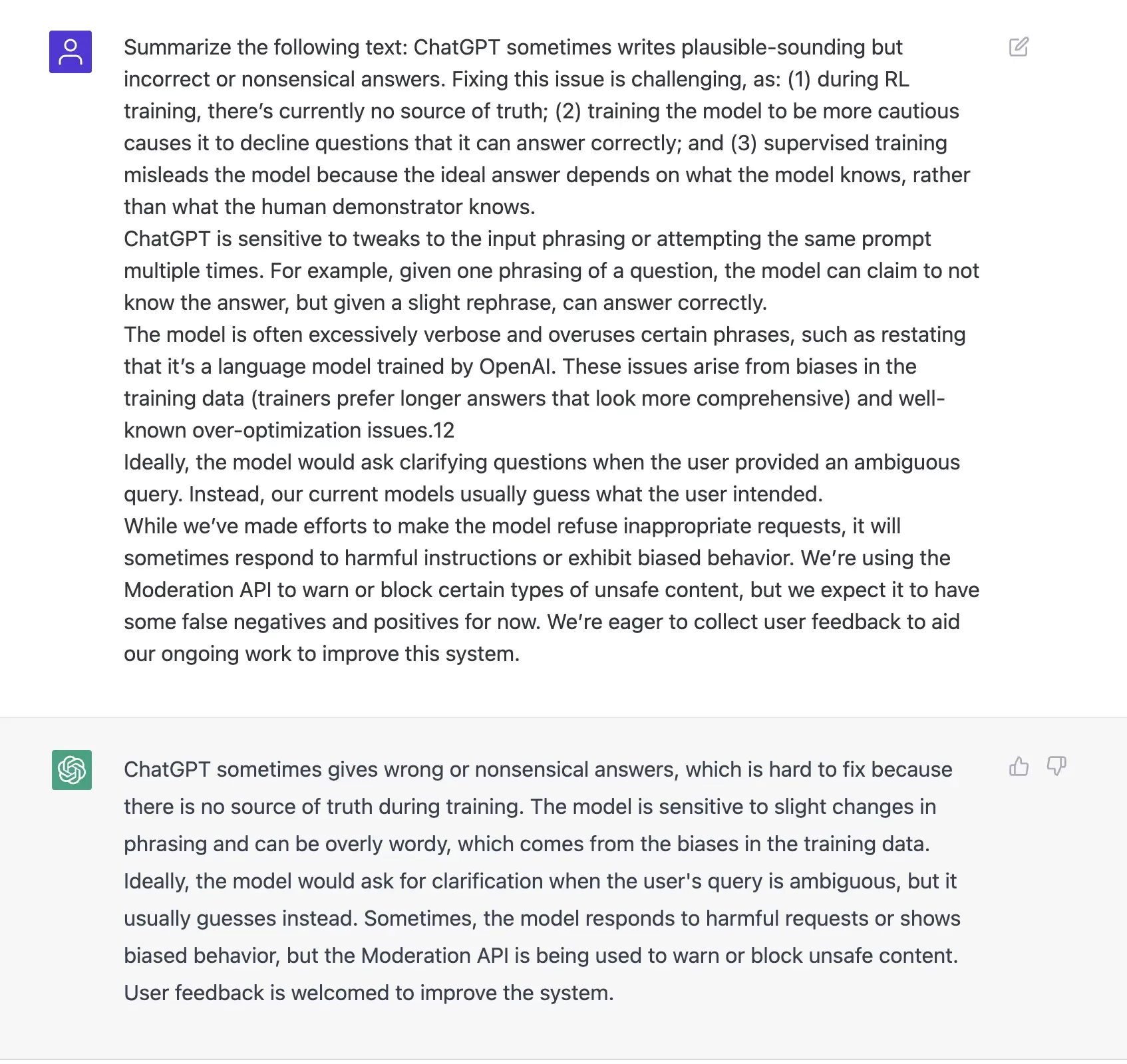
Whether you feel like your own content is too wordy or you want to quickly pull the main points from a longer piece of writing, a tool like ChatGPT can hack and slash a text into small digestible chunks. Just don’t forget to fact check. Below, we asked the bot to summarize a block of text found on the OpenAI website.
Early stage keyword research
AI models can be a great resource for broad keyword research, but you’ll still want to verify the output’s value with tools like Ahrefs, SEMRush, and Google Search Console. ChatGPT’s lack of access to post-2021 data and issues with inherent bias mean it might not be the right tool for a deep dive, but if you’re in a creative rut or lack familiarity with all the details of a product, OpenAI’s model can help fill in blanks you may not have considered on your own.

Extract keyword ideas from content
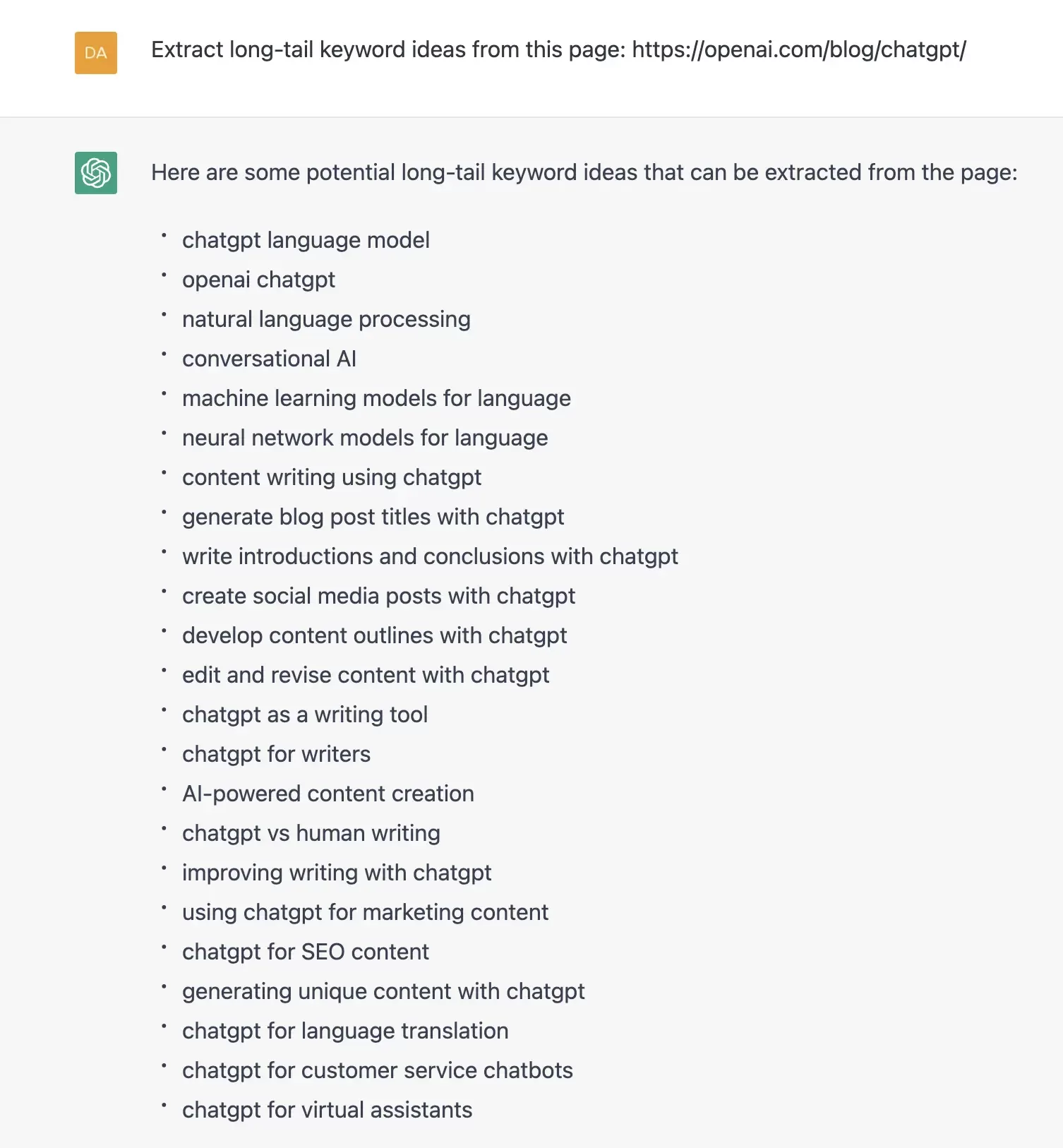
Take competitor analysis to the next level by having your AI assistant analyze and extract top-performing keywords from successful competitor content. For the most relevant results, we recommend specifying that you’re looking for long-tail keywords. In this example, we asked ChatGPT to extract keyword ideas from OpenAI’s site itself.
Advanced tips for leveraging ChatGPT
For users who have already mastered the basics, we have a few advanced tips for getting the most relevant output from powerful AI tools like ChatGPT.
Set the context
To get the best results, be as specific as possible in your requests. For example, if you’re a digital marketing agency doing keyword research for your homepage copy, try to be as specific as possible about your services and target audience.

Ask the bot to think outside the box
If you feel like the output you’re getting is too general or isn’t going to add anything new to a popular topic, ask the bot to give you uncommon ideas or ideas most people haven’t already considered.
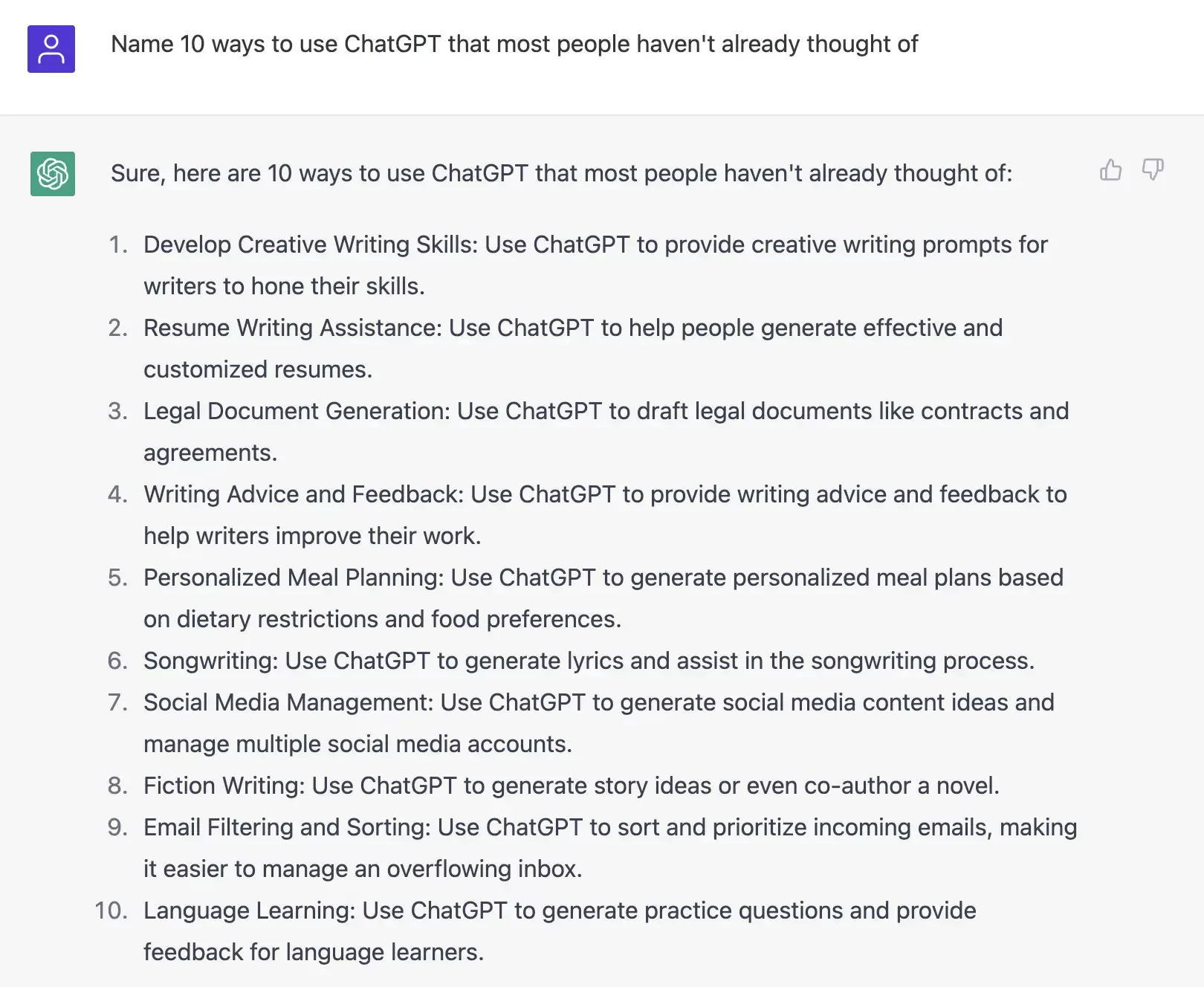
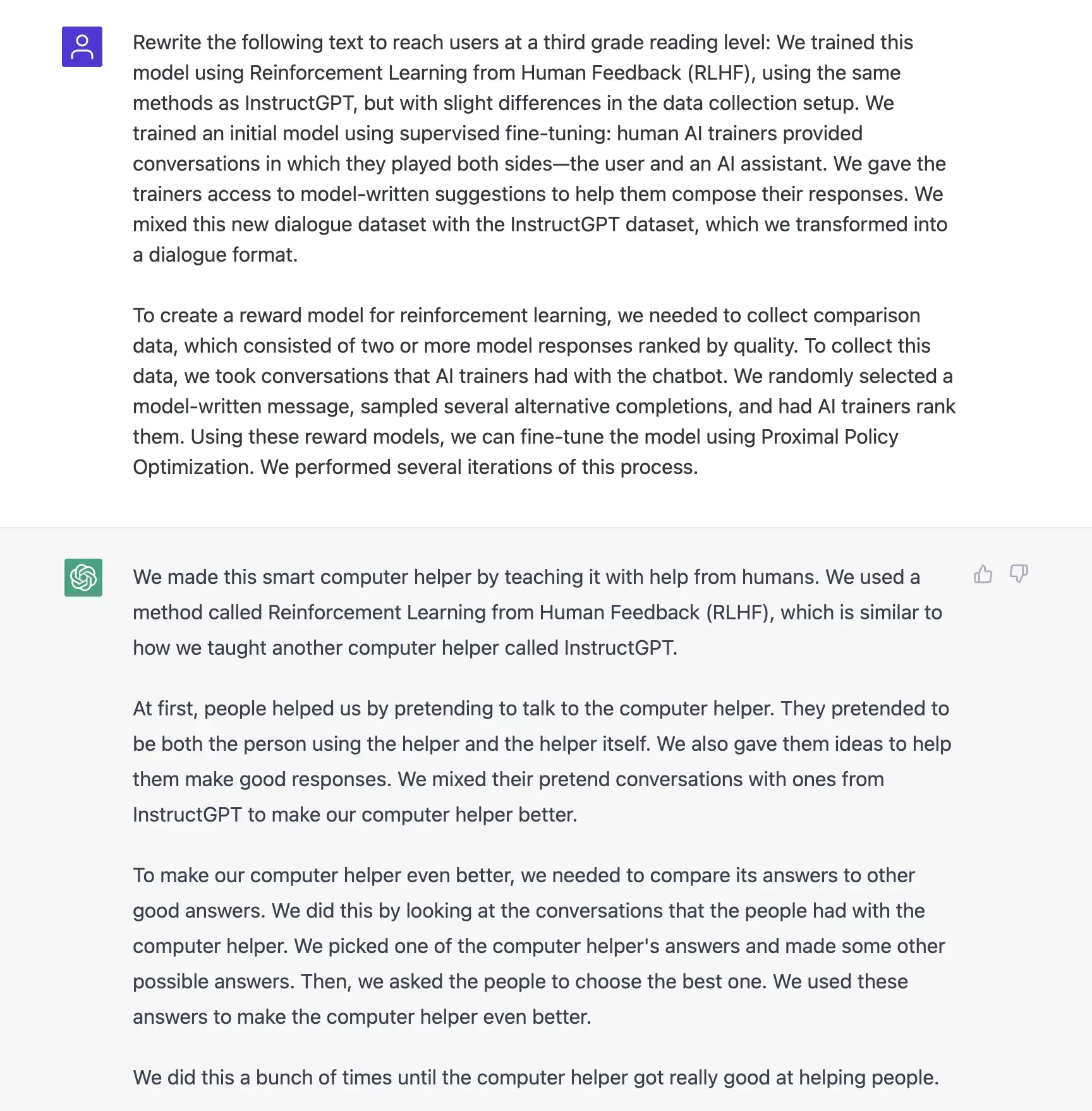
Specify your audience’s level of reading comprehension
This tip is especially useful when you need to simplify technical language.
Conclusion
Words of wisdom from OpenAI’s CEO himself: “fun creative inspiration; great! reliance for factual queries; not such a good idea.”
Free SEO Scorecard
Get professional analysts' insights into your Technical SEO, Content, Competitor Activity, UX, Web Analytic Configuration, and more. Get started with your free website SEO audit today.

