4 Tips to Optimize for User Intent: Target the Right Traffic
It's easy to get deep in the weeds analyzing which keywords to optimize for based on search volume and competition. However, it's important to take a step back and think about what your target audience really wants.
Optimizing for user intent—or search intent—simply means centering your digital marketing services around the true intentions of each search. And if you forget to assess what your target audience is searching for and which results search engines are populating for those queries, you run the risk of missing the point.
By harnessing user intent, you can attract the right audiences who are more likely to convert. Let's review.
Understand the Three Types of Search Intent
Search intent is typically categorized into three buckets:
- Informational
- Navigational
- Transactional
Informational and navigational searches are classified as low intent, meaning searchers usually aren’t close to converting and therefore aren’t seen as qualified prospects. However, transactional searches have high intent keywords which signify the user is more likely to complete a transaction.
Informational Searches
People use search engines frequently to find information. When someone is looking for information, they tend to search questions, but informational searches can also be posed as statements. Here are a few examples of informational searches:
- “How deep is the ocean?”
- “Why does my stomach hurt?”
- “Banana bread recipe”
Navigational Searches
People use navigational searches when they’re looking for a particular website. They’ll typically include the brand name in their query as well as a product, service, or something specific to that website. Below are several examples of navigational searches:
- “Instagram user login”
- “Workshop Digital SEO”
- “Nike”
Transactional Searches
Transactional searches happen when a user is considering making a purchase. When a person is ready to buy, they’ll usually search for the specific product or service and sometimes include the brand name. Here are different types of transactional searches:
- “Nordstrom dresses prices”
- “Cheap Macbook pro”
- “Buy all-weather outdoor furniture”
Let Google Give you the Answers
When analyzing search intent, the best tip to remember is to let Google do the work for you. On average, Google handles 3.8 million searches per minute, and its massive database has a plethora of information stored to serve up for individual queries.
Keep in mind…
The main goal of search engines is to serve up the most relevant information for each specific query.
This is why Google’s algorithm undergoes constant updates. These updates improve the process of retrieving the best and most relevant answers for users. Essentially, Google and other search engines are working the hardest to understand search intent, which means we can learn from their insights!
Manually Analyze SERPs
Take your list of keywords and search them manually. What is coming up in search results pages? Does Google retrieve resources that are relevant to your website? You may have “custom dog collars” on your list but adjust it depending on what comes up when that phrase is searched. You want to ensure that your keywords populate content specific to your industry and target audience.
Check Featured Snippets
Search engines will display featured snippets depending on the query and whether it was informational, navigational, or transactional. For example, high intent keywords similar to “buy” and “shop” are more likely to generate product carousels while low intent keywords (informational and navigational searches) are more likely to bring up featured snippets:
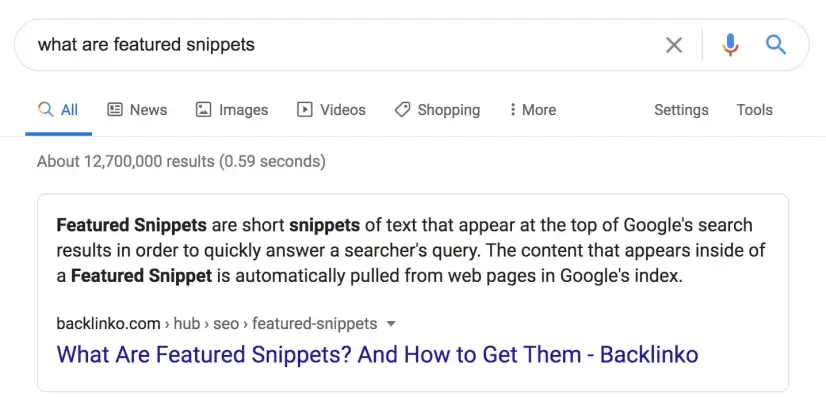
Featured snippets currently appearing for your target keywords should influence the way you write content and optimize your website in general. We’ll dive deeper into content style in a section below.
Identify Gaps in Content
An effective method to attract the right traffic is to provide answers where content “gaps” exist, meaning there are opportunities to provide more content where information is lacking. Search some of your target keywords again to see if enough information is available for each keyword, and if not, write content for that query.
Find Related Keywords in “People also ask”
Within search results pages, you’ll sometimes see a box called “People also ask.” This box contains queries similar to the keyword you searched. Always be sure to review this resource because it can provide you with related keywords to optimize for on your website:

Learn from Top-Ranking Pages
Since Google is serving up the most relevant results, we can study the top-ranking pages to determine qualities that make them valuable to search engines. Although it’s tempting to reinvent the wheel with every website and piece of content, it is much more effective to study what’s already successful when trying to optimize for user intent.
What Type of Content?
First of all, take note of whether the content is text or a video. If the content is text, then identify whether the text is a blog post, landing page, product page, or something different. This will help you understand the style of content search engines are serving for a specific keyword as well as what users are typically expecting to see.
How is the Content Formatted?
When analyzing top-ranking pages, you’ll also want to check how the content is formatted. For example, is the content a recipe, step-by-step guide, review, opinion piece, or something else? Let’s look at SERPs for “summer gardening tips”:
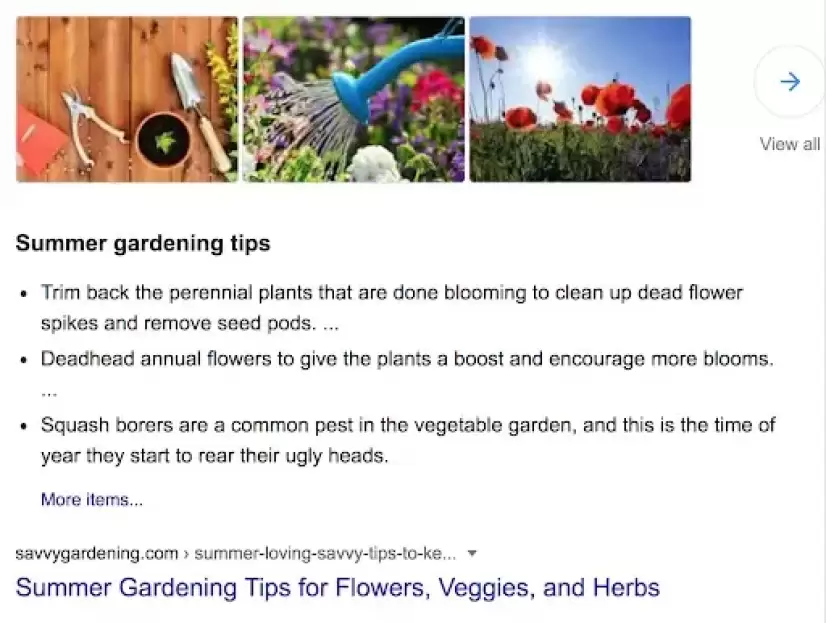
This article is showing up as a featured snippet and it’s closest to a step-by-step guide. If you’re optimizing content related to gardening, it’s important to see how other gardening websites are formatting their pages.
Does it have Structured Data?
Structured data provides search engines with additional context for the purpose of a page. It also can qualify content to show up in SERPs as rich snippets.
This free structured data testing Chrome extension allows you to pinpoint structured data implemented on any website. While visiting the top-ranking pages, be sure to check this tool to see if any structured data has been utilized. Whether it’s Organization, Local, FAQ, or another type of schema markup, you should be letting the structured data on the top-ranking pages guide your approach.
Take Advantage of Time-Saving Tools
While manually reviewing SERPs, checking featured snippets, identifying content gaps, and looking at how content is formatted are all helpful, tools exist that can make these processes more efficient.
Below are a few handy tools that you can pay to use—as well as several that are free!
- Ahrefs
- Explore target keywords and find similar terms
- Discover search features for specific keywords
- Conduct SERP analysis
- Find gaps in content
- Check backlinks and more!
- SEMRush
- Explore target keywords and discover related queries
- Analyze SERPs by looking at pages ranking for target keywords as well as featured snippets
- Find gaps in keywords and content
- Review backlinks and more!
- Answer the Public (Free)
- Navigate through various queries people search to discover new keywords and understand search intent
- Google Trends (Free)
- Track data for keywords over different periods of time and in many regions
- Compare keyword trends
- Quora (Free)
- See real-time questions people are asking to find new content ideas
Target the Right Traffic with a Digital Marketing Team
Optimizing for search intent isn’t always intuitive and it doesn’t happen overnight. People aren’t easy to understand, so sometimes we have to navigate confusing queries to find what people truly want when they search.
Many of these strategies also take time to complete and can be ongoing tasks. If you’re interested in talking to digital marketing experts on how to optimize for your specific target audience, reach out to our team today.
Boost your customer acquisition goals with SEO
Learn how to assess and optimize your website performance with this guide.

